Table of Contents
- What is Coal? - WorldAtlas
- Britain’s Record Coal Free Run Ends After 18 Days | usave.co.uk
- FOSSIL FUELS - COAL
- Heritage Railway Association supports last gasp bid to save UK coal
- What to consider when doing your Coal Due Diligence - Landmark Academy
- Coal Pension Trustees hires Unilever CIO | News | IPE
- Australia's new citizenship test: swear allegiance to Queen and Coal ...
- The End of Coal is in Sight - COP26 Update - Acuity Law
- Significant growth in coal sector due to rise in output of fossil fuel ...
- What is coal? - Origin Energy



What is Coal?



Uses of Coal

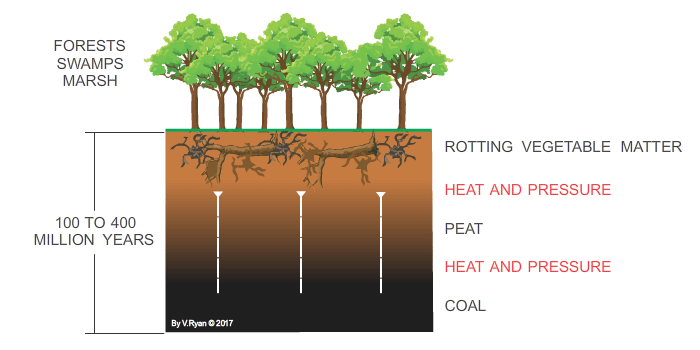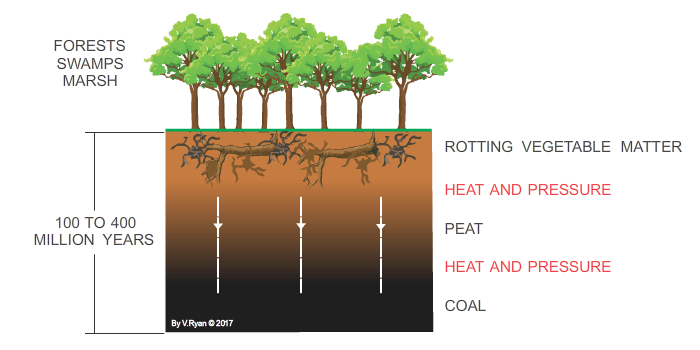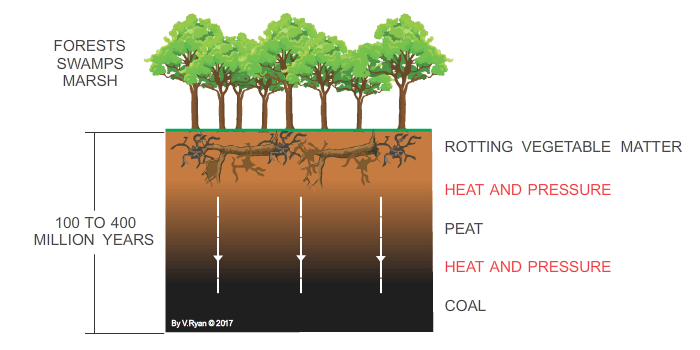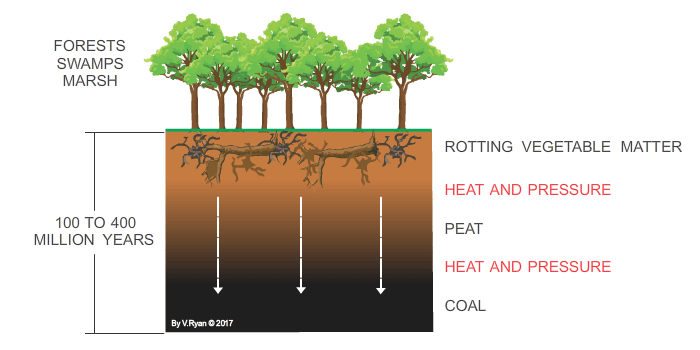
Types of Coal
Coal is classified into four main types based on the carbon content and heat value: - Lignite: Also known as brown coal, lignite has the lowest carbon content and is used primarily for electricity generation. - Subbituminous Coal: This type has a higher carbon content than lignite and is used for both electricity and industrial processes. - Bituminous Coal: With a higher carbon content and higher heat value, bituminous coal is used for electricity generation, industrial processes, and for producing coke for steel production. - Anthracite: The rarest and most valuable type, anthracite has the highest carbon content and is used for residential and commercial space heating.
Pollution and Environmental Impact
The extraction, transportation, and combustion of coal have significant environmental and health impacts: - Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Coal combustion releases large amounts of carbon dioxide, a major contributor to global warming. - Air Pollution: Coal burning releases sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter, contributing to air pollution and negative health effects. - Water Pollution: Coal mining can lead to water pollution through the release of heavy metals and other pollutants.